GitLab Service
The GPU cluster runs a self-hosted GitLab instance. Like with the web services from GitLab.com and GitHub.com, users can pull and push code to and from remote repositories. The version control software used to do all this is called Git.
Contents
Create an account
Using a web browser, access the GitLab page, then create an account following the on-screen instructions.
Pushing to remote
Windows client
Create or copy a repository as with normal Git workflow, then:
git remote add origin 147.8.193.174:9171/[username]/[reponame]git push --set-upstream origin master- You will be prompted for your GitLab credentials, if entered correctly it will push your local to the remote, creating a new remote repository if necessary. Subsequent pushes do not require credential input.
- If you have trouble authenticating, check if your correct user name is being used. Set it explicitly using
git remote set-url origin http://<username>@147.8.193.174:9171/<username>/<reponame>.git
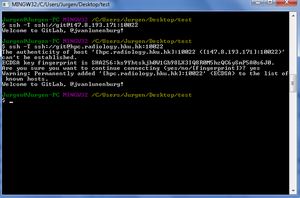
Pushing with SSH key
- Add a public SSH key (e.g. RSA type generated by
ssh-keygen) to your GitLab profile using the web interface. - Add your private key to your client git's
.sshfolder. If it doesn't exist, create the folder. E.g. for the Windows git MSYS commandline docd ~/andmkdir .ssh, then copy the private ssh key into it. - Test the key by running
ssh -T git@147.8.193.174from Git Bash. You should get a personalised welcome message. - Now the remote add line from above becomes:
git remote add origin git@147.8.193.174:<username>/<reponame>.git
`
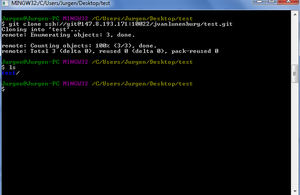
Pulling from remote (demonstration)
Access Management and Sharing
You can set repositories to private and invite users with different permission levels. You can invite either individually or in bulk via a Group.
Alternatively, you can move your repository to a Group namespace (e.g. Radiology), in which case member access depends on their Group Role. Depending on your own role in that Group, you may lose some admin-related rights for the repository.
If you are not part of a (private) Group, request with a Group Owner to be added. For public Groups you can use the GitLab "explore groups" feature to make a request.